As demand rises for premium dairy fat products like cream, butter, and ghee, producers require hygienic, efficient, and scalable systems to meet growing consumer expectations. GOMA Engineering provides turnkey solutions that cover the complete production cycle—from milk separation and fermentation to pressing, melting, and packaging. Whether producing white butter, table butter, or ghee from cream or butter, our fully automated systems deliver high product yield, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
Industry Insights
Butter is a widely consumed dairy product extracted from milk or cream fats. With rising usage in foodservice, confectionery, and bakery sectors, its market has seen a CAGR of 21%.
Ghee, deeply rooted in Indian tradition, is used in cooking, Ayurveda, and rituals. The ghee market was valued at INR 2,273 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach INR 4,653 billion by 2024.
Cream, separated from whole milk, is used in savory dishes, desserts, and culinary bases. The cream segment is growing at a CAGR of 11% in the food processing sector.
.png)
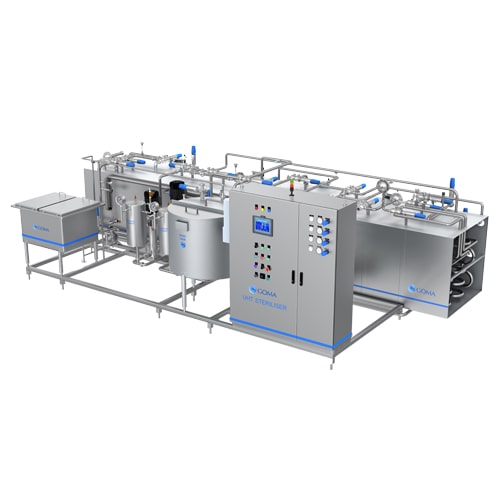

Functionality:
1) Heats cream to 85°C for 15 seconds to eliminate harmful microbes.
2) Designed for controlled heating and rapid cooling cycles.
3) Constructed with food-grade SS304/316 for hygienic processing.
4) Equipped with automated control panel for temperature and flow regulation.
Benefits:
1) Ensures food safety and extends shelf life.
2) Maintains product quality for further processing.
3) Meets mandatory dairy pasteurization standards.
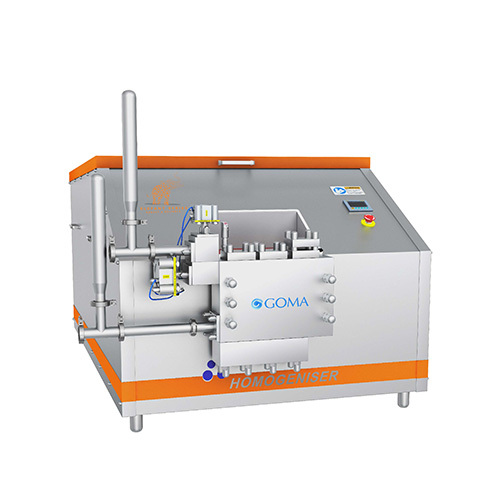
Functionality:
1) Breaks down fat globules in cream using high-pressure homogenization.
2) Provides uniform emulsion for stable cream.
3) Built with robust SS construction for durability.
4) Equipped with automated control panel for temperature and flow regulation.
Benefits:
1) Ensures food safety and extends shelf life.
2) Maintains product quality for further processing.
3) Meets mandatory dairy pasteurization standards.
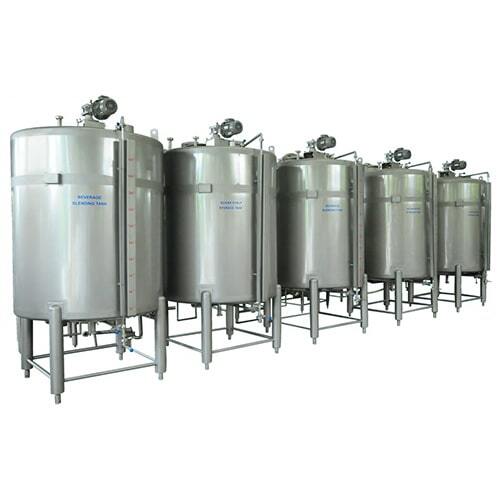


Functionality:
1) Stores pasteurized cream or melted butter at required temperatures.
2) Varying capacities available to suit plant size.
3) Double-walled insulated SS design for temperature control.
4) Control system for monitoring storage conditions.
Benefits:
1) Maintains product integrity between stages.
2) Supports continuous production.
3) Prevents contamination during intermediate holding.
Functionality:
1) Shapes and extrudes butter into blocks or portions.
2) Adjustable capacity for different production scales.
3) Precision-built SS structure for uniform shaping.
4) Automatic control unit for portioning accuracy.
Benefits:
1) Maintains hygiene in final packaging.
2) Extends shelf life of finished products.
3) Enhances brand presentation and consumer appeal.
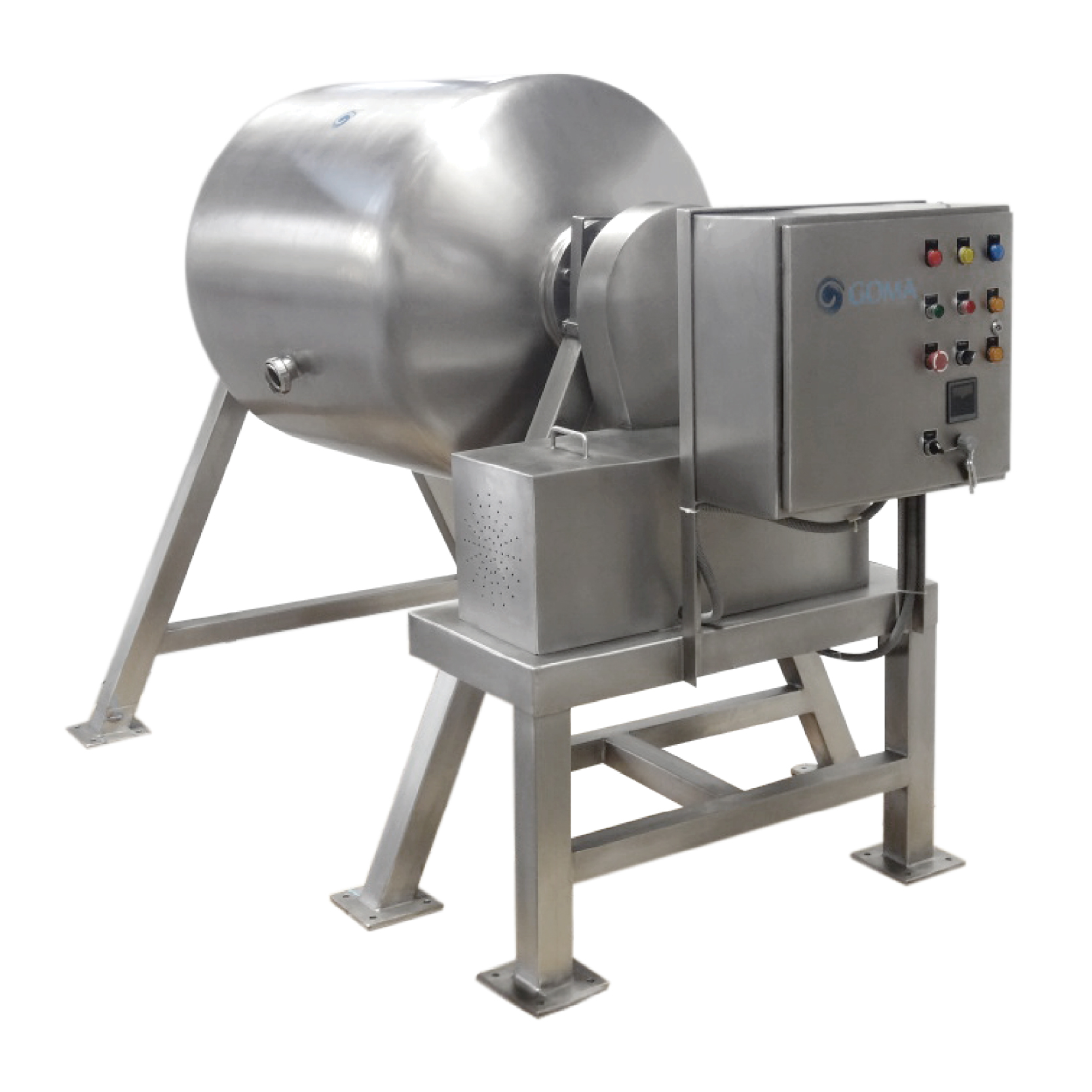
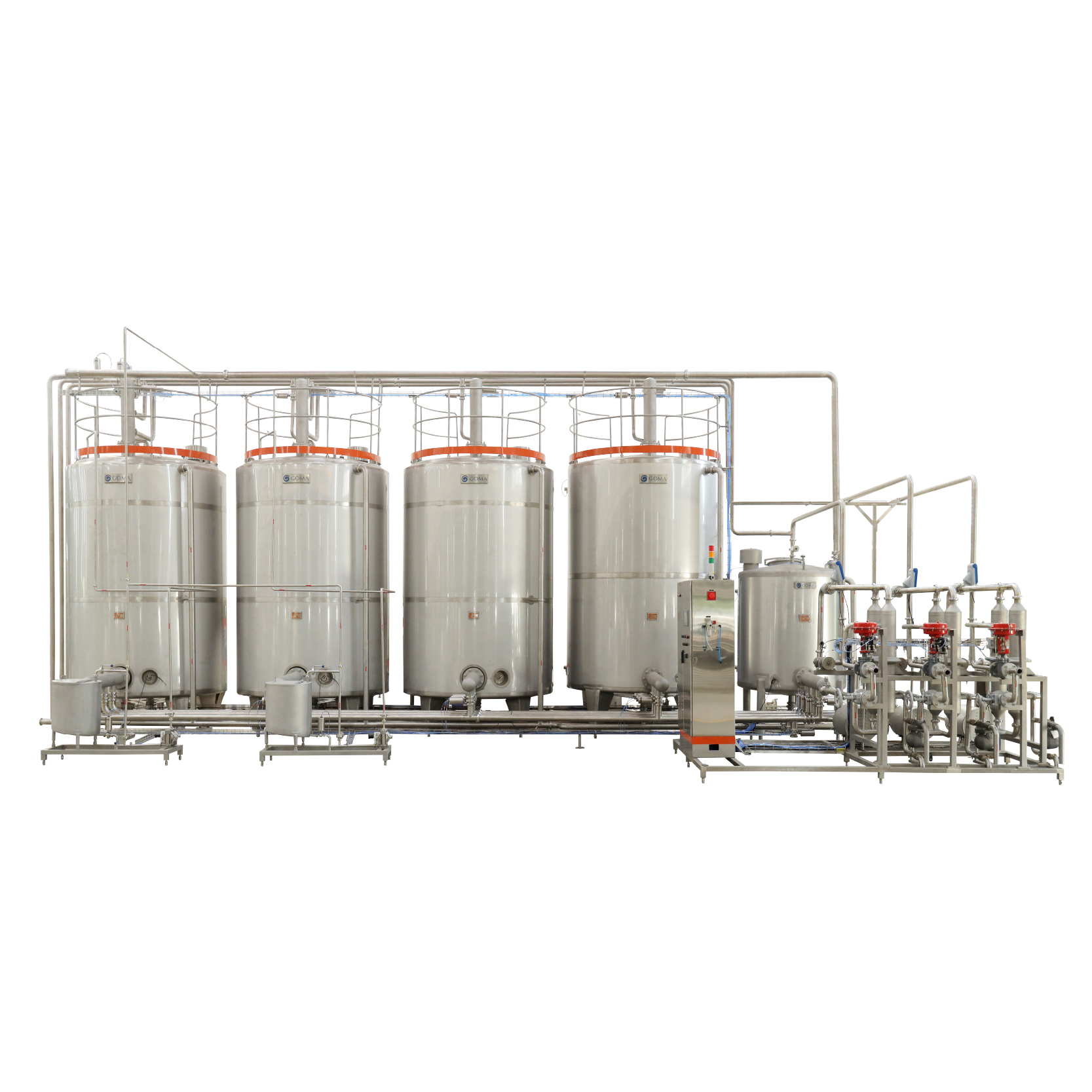


Functionality:
1) Automated cleaning of tanks, pasteurizers, and pipelines.
2) Available in single-tank or multi-tank options.
3) Constructed in SS316 with spray ball technology.
4) PLC panel for cycle programming and monitoring.
Benefits:
1) Saves utilities and reduces downtime.
2) Maintains hygiene without dismantling equipment.
3) Ensures compliance with food safety standards.
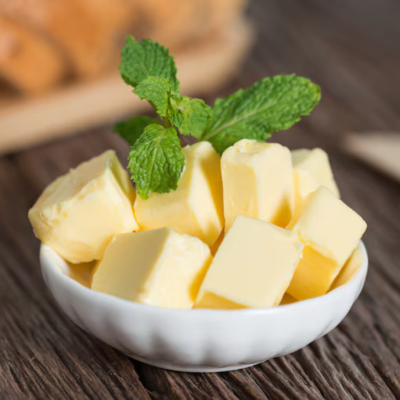

Processed from pasteurized cream, this salted or unsalted butter is ideal for direct consumption and foodservice applications.
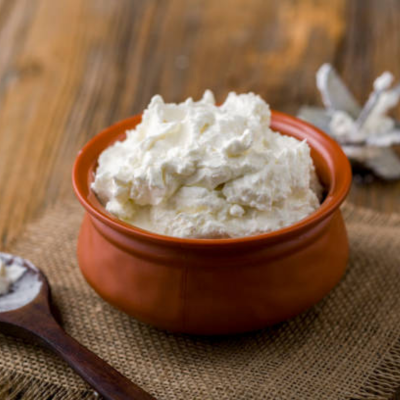

A traditional, unsalted variety of butter made from cultured or fresh cream, commonly used in Indian households and regional recipes.
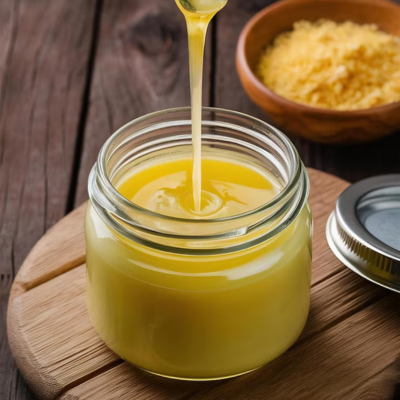

Clarified butter produced either directly from cream or by further processing white or table butter, offering rich taste and extended shelf life.

Creams enhanced with natural cultures or Flavors, used in premium culinary and dairy formulations.

Ghee infused with herbs or spices to meet evolving consumer demand for functional and gourmet variants.